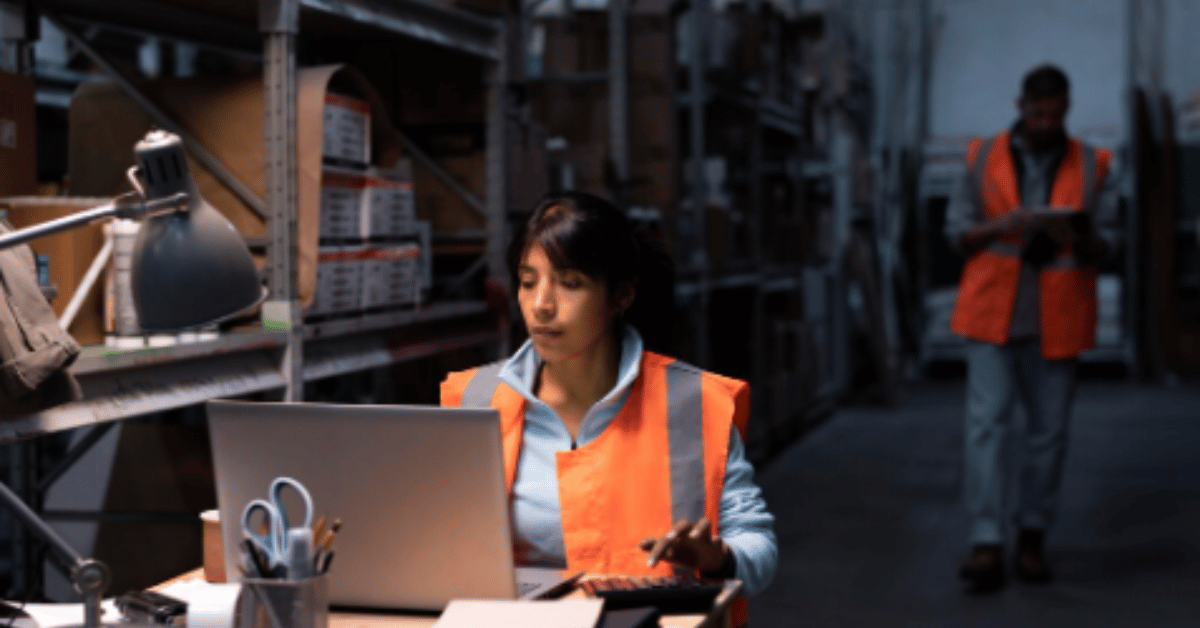
In today’s fast-paced supply chain landscape, businesses are continuously seeking innovative ways to optimize efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. E picking, or electronic picking, has emerged as a cornerstone of modern warehouse operations, fundamentally transforming how goods are located, selected, and prepared for shipment. At its core, e-picking leverages technology, ranging from barcode scanners and RFID systems to wearable devices and automated picking software, to streamline the selection process and reduce human error. For businesses, this translates into faster order fulfillment, higher customer satisfaction, and improved inventory control. Within the first 100 words, it is crucial to understand that e-picking is not merely an incremental upgrade to traditional methods; it represents a paradigm shift in warehouse logistics, redefining roles, responsibilities, and the very flow of goods from storage to shipment.
Beyond speed, e-pickings provides comprehensive tracking capabilities, enabling managers to monitor every step of the picking process in real-time. The integration of advanced software platforms ensures that data on stock levels, pick rates, and worker performance is accurately captured, creating actionable insights for decision-making. “Accuracy in inventory is the heartbeat of e-commerce efficiency,” notes logistics consultant Maria Sanders, emphasizing the critical role of technology in modern warehousing. Moreover, the adoption of e-picking aligns closely with sustainability goals, as optimized routes reduce unnecessary movement and energy consumption. In essence, e-picking is not just a tool; it is a strategic investment that equips warehouses to meet the demands of the digital economy while maintaining operational excellence.
Understanding E-Picking Technology
E-picking technology encompasses a range of tools designed to enhance the pickings process. Traditional manual picking relied on printed pick lists, human memory, and visual scanning, which were prone to errors and inefficiencies. Modern e-pickings systems, however, integrate hardware and software solutions to automate and guide the picker through the warehouse efficiently. Barcode scanners, RFID readers, and mobile devices communicate with warehouse management systems (WMS) to provide real-time updates on inventory, reducing mistakes and optimizing labor. This technology also enables dynamic task allocation, where workers are assigned picking tasks based on proximity, skill, and workload, thereby minimizing idle time.
Voice-directed picking’s another popular e pickings approach, allowing workers to receive instructions through headphones, keeping their hands free for faster operation. Similarly, wearable devices like smart glasses provide augmented reality overlays that indicate the exact location of products on shelves. These innovations collectively ensure that warehouse staff can achieve higher pick rates while minimizing errors. “Technology does not replace the worker; it empowers them,” explains operations manager Jason Lee. E picking’s not a uniform solution; businesses can customize systems based on warehouse size, product type, and order complexity.
Table 1: Key E-Picking Technologies and Their Benefits
| Technology | Functionality | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Barcode Scanners | Scans product codes for accurate picking | Reduces errors, tracks inventory |
| RFID Systems | Tracks items via radio frequency tags | Real-time location, faster processing |
| Mobile Devices | Interfaces with WMS for pick instructions | Improves efficiency, reduces paperwork |
| Voice Picking | Provides audio instructions to workers | Hands-free operation, increased speed |
| Wearable AR Devices | Displays pick location and instructions visually | Enhances accuracy, reduces training time |
Advantages of E-Picking in Modern Warehousing
The implementation of e-pickings delivers measurable advantages across operational, financial, and customer-facing domains. One of the primary benefits is accuracy. Traditional paper-based picking methods often resulted in mis-picks, leading to returns, dissatisfied customers, and increased costs. E-pickings minimizes these errors by providing step-by-step guidance, automated verification, and real-time feedback. Warehouses adopting e-picking have reported error reduction rates exceeding 50%, which directly impacts profitability and customer trust.
Another advantage is efficiency. E-pickings technologies optimize routes within the warehouse, allowing pickers to complete tasks faster while conserving energy. Integration with WMS ensures that inventory updates occur immediately, preventing double-picking or missed orders. The flexibility of e-pickings also supports scalability, as warehouses can easily adjust to fluctuations in demand, particularly during peak seasons or promotional events. Logistics strategist Daniel Ortega notes, “E-pickings transforms warehouses from reactive spaces to proactive command centers, capable of adapting instantly to customer needs.” Beyond operational gains, e-picking enhances worker satisfaction by reducing physical strain and cognitive load, fostering a safer and more productive environment.
Table 2: Operational Impact of E-Picking vs. Manual Picking
| Metric | Manual Picking | E-Picking | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pick Accuracy | 92% | 99.5% | +7.5% |
| Order Processing Time | 45 mins/order | 28 mins/order | -38% |
| Worker Fatigue | High | Moderate | Improved |
| Inventory Tracking Accuracy | 85% | 99% | +14% |
| Customer Satisfaction | 88% | 97% | +9% |
Integration With Warehouse Management Systems
For e-pickings to function optimally, it must integrate seamlessly with warehouse management systems (WMS). WMS platforms act as the brain of warehouse operations, centralizing inventory data, tracking orders, and orchestrating picking activities. E-picking systems communicate with WMS to assign pick tasks dynamically, verify stock availability, and update inventory in real-time. This integration ensures that pickers always have accurate, up-to-date information, minimizing errors and optimizing workflow.
Advanced WMS platforms also incorporate analytics, enabling managers to monitor key performance indicators such as pick rate, route efficiency, and worker productivity. Insights derived from this data inform strategic decisions, such as reconfiguring warehouse layouts or implementing additional automation. “A well-integrated system eliminates guesswork, turning warehouses into precise operational hubs,” explains logistics analyst Karen Wu. Moreover, cloud-based WMS allows remote monitoring and real-time reporting, providing managers with the flexibility to oversee multiple facilities from a single location, further enhancing operational oversight and efficiency.
Types of E-Picking Systems
E-pickings systems can be categorized into several types based on the technology employed and the nature of warehouse operations. Barcode-based picking remains one of the most common solutions, where pickers scan items using handheld devices or mobile scanners. This method provides immediate verification, reducing the likelihood of picking errors. RFID-enabled picking is another sophisticated approach, leveraging radio frequency identification to track items in real-time. Unlike barcode systems, RFID does not require line-of-sight scanning, enabling bulk verification and faster processing, particularly in high-volume warehouses. Voice-directed picking guides workers through their tasks via audio instructions, allowing hands-free operations and minimizing distractions, which is especially beneficial in large facilities. Augmented reality (AR)-assisted e-picking represents the latest evolution, projecting pick paths and item information directly into wearable displays, significantly reducing search time and errors.
Hybrid systems are increasingly popular, combining multiple technologies to leverage the strengths of each. For example, a warehouse may implement RFID for inventory scanning, barcode verification for final confirmation, and voice instructions for guiding pickers. Such integration creates a highly flexible environment capable of adapting to varied product types, order sizes, and seasonal fluctuations. This ensures consistent operational efficiency while optimizing labor allocation. Logistics consultant Rachel Turner emphasizes, “The best e-picking systems are those that align technological capability with human efficiency, rather than trying to replace the workforce entirely.” Customization and adaptability remain central to realizing the full potential of e-picking solutions in modern supply chains.
Implementation Strategies for E-Picking
Implementing e-picking requires careful planning and strategic alignment with overall warehouse operations. The process begins with assessing warehouse layout and workflows, identifying high-traffic areas, common pick routes, and potential bottlenecks. Mapping these parameters helps determine the most suitable e-picking technology, whether that be barcode scanners, wearable AR devices, or voice-directed systems. Employee training is another crucial component; workers must be comfortable with new tools and confident in interpreting system instructions. Organizations often adopt phased rollouts, starting with a pilot zone to validate efficiency gains and identify operational challenges before full-scale deployment.
Integration with existing warehouse management systems is essential for data consistency and real-time updates. Additionally, businesses must establish protocols for system maintenance, software updates, and troubleshooting, ensuring minimal disruption during peak operations. Monitoring key performance indicators—such as pick accuracy, order fulfillment speed, and worker productivity—provides actionable insights for continuous improvement. Continuous feedback loops between technology, management, and staff ensure that e-picking systems evolve alongside operational demands. Logistics analyst Thomas Green notes, “Successful implementation is not just technological; it’s cultural. Staff buy-in, effective training, and iterative improvement define long-term success in e-picking adoption.”
Common Challenges in E-Picking and Their Solutions
While e-picking offers substantial advantages, warehouses can face challenges during adoption. System integration issues often arise, particularly in older facilities with legacy WMS platforms. Compatibility problems can result in delayed updates, inaccurate inventory data, and decreased efficiency. Addressing these challenges requires proper IT planning, software customization, and rigorous testing prior to deployment. Employee resistance can also pose barriers; some staff may perceive technology as a threat to job security or be hesitant to adapt. Structured training programs and clear communication about the benefits of e-picking—such as reduced workload, improved accuracy, and safer operations—help mitigate this resistance.
Another common concern is cost, particularly for small-to-medium enterprises. Initial investments in scanners, wearable devices, or AR systems can be significant. However, businesses should evaluate total cost of ownership and projected savings from reduced errors, faster fulfillment, and lower labor expenses. Security and data integrity are additional considerations, especially for cloud-based WMS platforms. Implementing robust access controls, encryption, and regular audits ensures operational and digital safety. “Challenges are inevitable, but with structured planning and employee engagement, e-picking can deliver exponential returns on investment,” notes warehouse operations consultant Lisa Morgan. By addressing these common obstacles proactively, organizations can unlock the transformative potential of e-picking technology.
Cost Analysis and ROI of E-Picking
Understanding the financial implications of e-picking is critical for warehouse decision-makers. Initial investments include hardware acquisition—such as scanners, AR devices, and RFID tags—software licenses, employee training, and integration costs. Depending on the warehouse size and complexity, these costs can range from tens of thousands to several hundred thousand dollars. Despite this, studies indicate that the return on investment (ROI) is achievable within a relatively short timeframe, typically 12–24 months, due to significant reductions in errors, improved productivity, and enhanced inventory management.
Indirect financial benefits include decreased employee turnover, lower training costs, and fewer returns or corrective shipments. Additionally, optimized picking routes reduce labor hours and operational expenses. Large e-commerce warehouses implementing full-scale e-picking often report productivity improvements of 20–40% and error reductions of over 50%. By combining direct cost savings with enhanced customer satisfaction and retention, the financial rationale for e-picking becomes compelling. CFOs and operations managers are increasingly viewing e-picking not as a capital expense but as a strategic investment in long-term competitiveness and scalability. “When evaluating technology, always look beyond the upfront cost; the efficiency gains and customer loyalty it fosters are invaluable,” advises financial analyst Robert Jenkins.
Future Trends in E-Picking
The future of e-picking promises continued innovation and integration with emerging technologies. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are being incorporated to predict demand, optimize pick paths, and allocate labor dynamically. AI algorithms analyze historical data, seasonal trends, and order patterns, creating predictive models that enhance operational efficiency. Robotics and autonomous picking systems are also becoming more prevalent, particularly in large fulfillment centers. Robots can navigate warehouse aisles, retrieve items, and deliver them to packing stations, working alongside human pickers for hybrid efficiency.
Augmented reality will continue to evolve, offering more immersive guidance and real-time error correction. Additionally, Internet of Things (IoT) devices will expand connectivity across warehouses, enabling sensors to monitor shelf weight, temperature-sensitive inventory, and item location in real-time. Sustainability will also be a focal point, with energy-efficient systems reducing warehouse carbon footprints. As supply chains grow increasingly complex, e-picking will transition from a technology option to a necessity for competitive differentiation, allowing companies to meet evolving customer expectations with speed, accuracy, and reliability.
Conclusion
E-picking represents a transformative evolution in warehouse logistics, shifting operations from manual, error-prone methods to technologically guided precision. By leveraging tools such as barcode scanners, RFID systems, wearable AR devices, and voice-directed instructions, warehouses can achieve higher accuracy, faster fulfillment, and enhanced worker productivity. Integration with WMS platforms ensures real-time inventory visibility, dynamic task allocation, and actionable performance analytics, providing a foundation for continuous improvement. While challenges such as cost, employee adoption, and system compatibility exist, structured implementation strategies, rigorous training, and careful planning mitigate these risks effectively.
The financial and operational benefits of e-picking are significant. Improved pick accuracy reduces returns, accelerates order processing, and enhances customer satisfaction. Efficiency gains lower labor costs, optimize workflows, and enable scalability, making e-picking a strategic investment rather than a mere technological upgrade. Looking ahead, advancements in AI, robotics, AR, and IoT will further enhance the capabilities of e-picking systems, offering predictive analytics, autonomous operations, and fully connected warehouse ecosystems. Ultimately, e-picking empowers businesses to meet the demands of the digital economy, delivering operational excellence, sustainability, and competitive advantage. As Maria Sanders observes, “E-picking is not just a warehouse solution; it is the blueprint for modern logistics excellence.”
FAQs
1. What is e-picking?
E-picking, or electronic picking, is the use of technology in warehouses to guide workers through the order fulfillment process accurately and efficiently.
2. What technologies are used in e-picking?
Key technologies include barcode scanners, RFID systems, voice-directed picking, augmented reality devices, and mobile interfaces integrated with WMS.
3. How does e-picking improve efficiency?
It optimizes pick routes, reduces errors, updates inventory in real-time, and enables dynamic task allocation, leading to faster and more accurate order fulfillment.
4. Is e-picking suitable for small warehouses?
Yes, scalable solutions exist for smaller operations, though the ROI and cost-benefit analysis should be carefully assessed.
5. What are future trends in e-picking?
Future trends include AI-driven task allocation, autonomous robotics, augmented reality guidance, IoT integration, and enhanced sustainability initiatives.